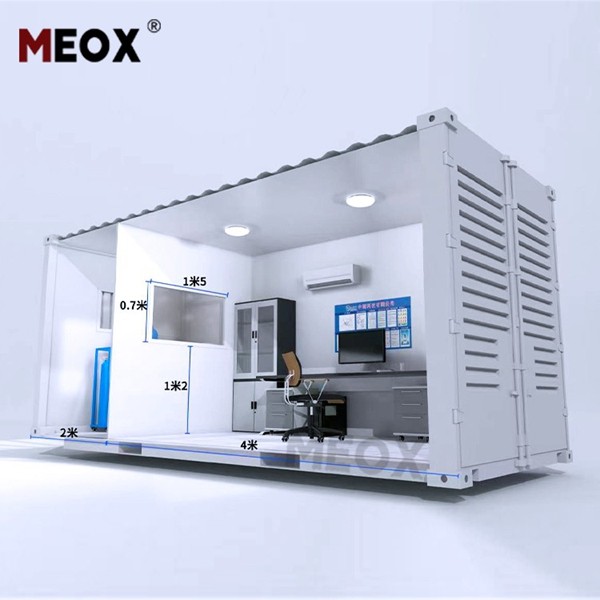
Growing plants in shipping containers is rapidly becoming a trend in urban agriculture, combining innovative technology with sustainable practices. Container farming leverages the structural advantages of shipping containers and modern agricultural techniques, resulting in efficient and productive farming solutions. Here’s a comprehensive guide for those interested in understanding the nuances of this unique farming method, focusing on experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
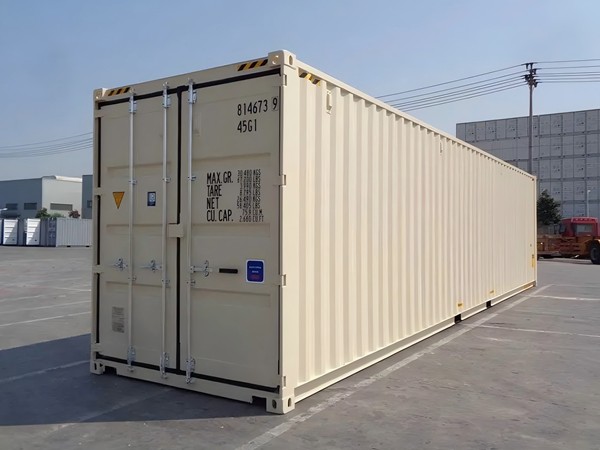

Shipping containers, originally designed for transporting goods across oceans, provide a solid, secure, and scalable option for plant cultivation. The robust structure protects against environmental factors, making them ideal for controlled agriculture. Start by understanding the basic modifications needed to transform a shipping container into a viable growing environment. Essential modifications include insulation, climate control, lighting, and irrigation systems.
A critical advantage of container farming is the ability to control every aspect of the growing environment. Climate control systems regulate temperature and humidity, essential for plant growth. Advanced LED lighting mimics natural sunlight, ensuring plants perform photosynthesis even in areas with limited natural light. Automated hydroponic or aeroponic systems can maximize water and nutrient use efficiency, supporting plant growth without the traditional soil medium.

Real-world experiences from experts reveal that while the initial setup can be capital intensive, the lower operational costs and higher yield outcomes balance the investment over time. Business models in urban areas are thriving, mainly due to the model’s ability to produce consistent crop cycles irrespective of seasonal changes. For example, farmers producing leafy greens find container farms profitable because they can supply fresh produce all year round.
From a professional standpoint, operators must possess expertise in both agriculture and technology. Understanding plant physiology, nutrient requirements, and pest management is crucial, as is the ability to operate and maintain automated systems. Platforms offering training resources and community forums are invaluable for new and experienced growers, enhancing knowledge sharing and problem-solving.growing plants in shipping containers
In terms of authoritativeness, container agriculture attracts endorsements from agricultural scientists and sustainability experts. Research from agricultural universities emphasizes container farming as a solution to overcome challenges faced by traditional farming methods. Concerns about land degradation, water scarcity, and food security can be mitigated through this model, highlighting its role in future food systems.
Trustworthiness in this context relates to the assurance of food safety and quality. Container farms typically operate under strict sanitary conditions, reducing contamination risks often associated with conventional farming. Transparency in farming practices, from seed selection to harvest, builds trust among consumers. Providing certification programs and adhering to organic standards further enhance credibility.
In recent years, several companies have emerged, specializing in building and selling turn-key container farms. These businesses focus not only on providing the infrastructure but also on supporting farmers with software solutions for data analysis and crop optimization. The use of sensors to monitor plant health and growth conditions allows for immediate adjustments ensuring optimal growth conditions at all times.
The sustainability angle of container farming cannot be overstated. By recycling unused containers, this model contributes to environmental conservation. Moreover, the localized nature of container farms reduces transportation emissions, as they can be placed close to urban markets, directly addressing the challenges of food miles.
In conclusion, growing plants in shipping containers offers a pragmatic approach to modern agriculture challenges. It combines structural, technological, and ecological benefits, making it an attractive option for urban farmers and entrepreneurs. As cities continue to grow and traditional farmland becomes scarcer, container farming presents a viable, scalable solution for sustainable food production. The continued evolution of technology will likely increase the efficiency and decrease the cost of these systems, broadening their accessibility and impact across the globe.