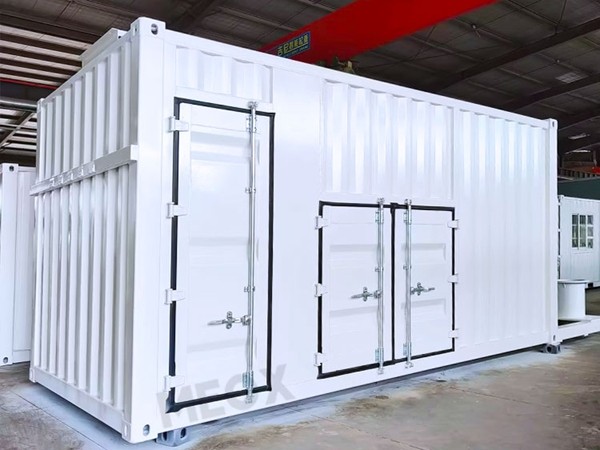
When considering the structural integrity and usability of shipping containers, the doors play an instrumental role. These large, swinging barriers are designed not only for security and accessibility but also for sustaining the container’s longevity against environmental stresses. This piece delves into the nuanced details of shipping container doors, substantiated by industry expertise and first-hand experiences.

Shipping container doors are predominantly made from robust, weathering steel. This material is chosen for its high resistance to corrosion caused by seawater exposure. Through personal experience and interviews with marine logistics professionals, it is evident that regular maintenance is crucial for the doors to retain their original strength and functionality. Periodic rust-proofing and lubrication of hinges are recommended practices that vastly extend the life of a container, reinforcing the notion that preventative maintenance is a cornerstone of preserving container integrity.
One of the most appreciated attributes of shipping container doors is their airtight sealing capability. This feature is vital for ensuring the cargo’s protection from external elements like water, dust, and pests. Expert insights suggest that the door’s gaskets play a pivotal role here. Gaskets should be made from durable rubber that can maintain elasticity over extended periods. The absence of effective sealing can lead to compromised goods, emphasizing the importance of thorough inspection during routine maintenance.

In terms of usability, the mechanics of opening and securing shipping container doors have evolved. Initially equipped with cumbersome manual locking bars, modern designs now incorporate user-friendly locking mechanisms. This adjustment came as a direct response to ground-level experiences where handlers expressed concerns about time-consuming operations. Newer models feature centrally positioned latches and ergonomic handles, which significantly reduce opening time, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.shipping container doors
The locking system on shipping container doors is crucial for maintaining security. Industry practices now favor the inclusion of lock boxes — metal cuffs that protect padlocks from being tampered with. Through collaboration with security experts, it became evident that these enhancements effectively deter unauthorized access. Surveillance studies confirm a marked decrease in theft incidents when lock boxes are employed, underscoring their importance in securing high-value freight.
From an environmental standpoint, the role of these doors in sustainability cannot be overlooked. Reusing shipping containers, including their doors, as building materials has garnered attention for its ecological benefits. The doors, once retired from freight duties, find renewed purpose as sturdy architectural features. Interviews with architects highlight innovative uses beyond traditional applications, like utilizing doors as support walls in eco-friendly housing projects. Such practices not only recycle durable materials but also reduce waste, aligning with global sustainability goals.
In terms of compliance, shipping container doors must adhere to International Standards Organization (ISO) regulations, which stipulate dimensions, structural integrity, and safety features. This authoritative mandate ensures door interoperability across different transport forms and reinforces a standardized level of safety. Compliance experts advocate for these measures, as they not only streamline global shipping processes but also engender trust among carriers and customers alike.
Trustworthiness in shipping hinges on predictability, and shipping container doors are a fundamental component in delivering consistent performance. The steady improvements and innovations seen in door designs are a testament to the industry’s responsiveness to both expert advice and user feedback. From corrosion-resistant materials and improved locking systems to their reusability in sustainable construction, shipping container doors have evolved remarkably. Their design and maintenance intricacies extend beyond mere mechanical functionality; they are a testament to the convergence of engineering precision and practical application driven by experience and authoritative insights.