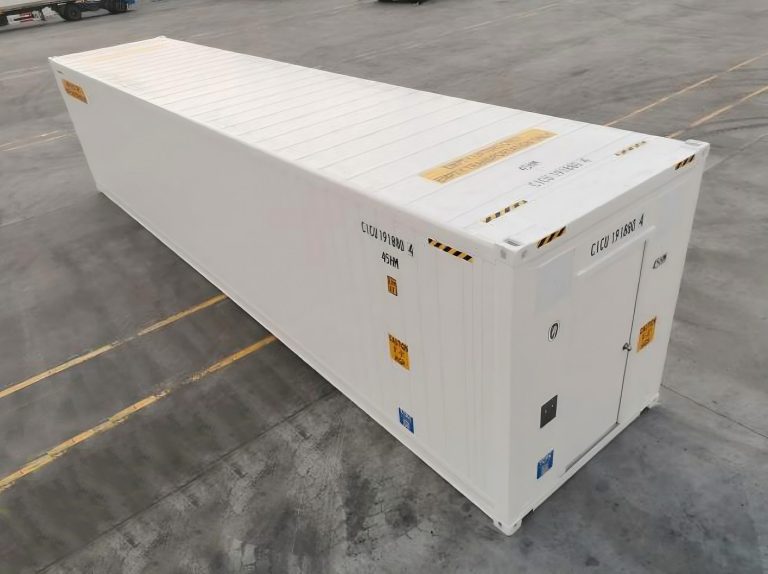
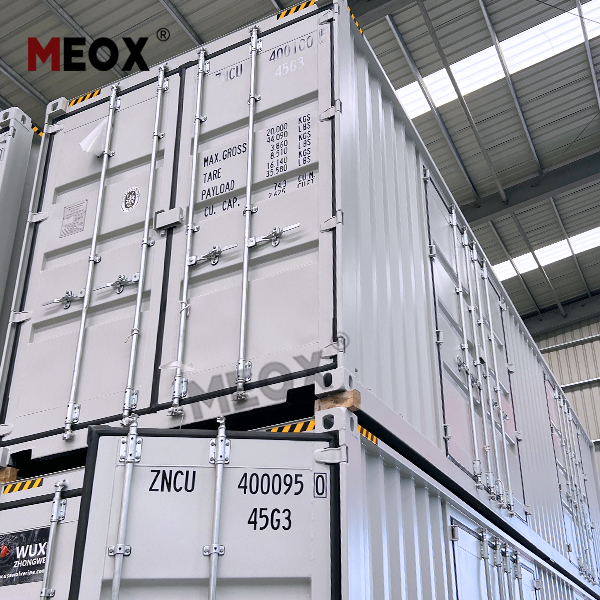
In the world of cold chain logistics, 40 reefer containers play a pivotal role in preserving the freshness and quality of temperature-sensitive goods during transportation. From perishable foods to pharmaceuticals, these containers rely on a consistent and reliable power supply to maintain optimal internal temperatures. Whether it’s a 40ft reefer container traversing the high seas or a 40 foot reefer on a long-haul truck journey, understanding their power requirements is essential for ensuring the integrity of the cargo. Incorrect power supply can lead to spoilage, financial losses, and damage to a company’s reputation.

Base Power Consumption of 40ft Reefer Container
The base power consumption of a 40ft reefer container is a fundamental aspect to consider. On average, a standard 40 foot reefer typically requires between 4,000 to 6,000 watts of power to operate its refrigeration system under normal conditions. This power is used to drive the compressor, fans, and other components that work in tandem to cool the interior of the container. The actual power consumption can vary depending on factors such as the set temperature, the external ambient temperature, and the insulation quality of the container. For example, if the 40 reefer container is set to maintain a very low temperature in a hot environment, it will consume more power as the refrigeration system has to work harder to counteract the heat influx. Understanding this base power consumption helps operators plan their power sources and ensure a stable supply to keep the cargo chilled.
Power Source Options for 40 Reefer Container
There are several power source options available for 40 reefer containers. One common option is shore power, which is used when the container is docked at a port or a terminal. Shore power provides a reliable and consistent electricity supply, ensuring that the 40 foot reefer can maintain its temperature without interruption. Another option is generator sets. Diesel generators are often used for 40ft reefer containers during overland transportation or when shore power is not available. These generators can be mounted on the truck or trailer carrying the container, providing an independent power source. Additionally, some modern 40 reefer containers are being equipped with hybrid power systems that combine diesel generators with battery banks or even solar panels, offering more flexibility and energy efficiency. Each power source has its own advantages and limitations, and choosing the right one depends on the specific transportation route, duration, and availability of infrastructure.
Peak Load and Surge Requirements of 40 Foot Reefer
40 foot reefer containers have peak load and surge requirements that operators need to be aware of. When the refrigeration system starts up, it often requires a higher amount of power for a short period, known as a surge. This surge can be up to three times the normal running power of the 40ft reefer container. During hot weather or when the container has been opened frequently, the refrigeration system may also experience peak loads as it works to cool the interior back to the set temperature quickly. To accommodate these peak loads and surges, power sources need to have sufficient capacity. For example, if a generator is being used to power a 40 reefer container, it should be sized appropriately to handle the surge current without tripping or failing. Failing to account for these peak load and surge requirements can lead to power outages and temperature fluctuations inside the container, endangering the cargo.
Power Connection and Compatibility for 40 Reefer Container
The power connection and compatibility of a 40 reefer container are crucial for seamless operation. These containers usually come with standardized power connection sockets, such as CEE (Combined European Electrical) sockets, which are designed to connect to different power sources. However, it’s important to ensure that the voltage, frequency, and phase of the power source match the requirements of the 40 foot reefer. For instance, most 40ft reefer containers operate on 480 volts, three-phase, 60 Hz power in North America, while in Europe, the standard may be 400 volts, three-phase, 50 Hz. Mismatched power connections can damage the refrigeration system of the 40 reefer container or prevent it from operating altogether. Additionally, proper grounding of the power connection is essential to prevent electrical hazards and ensure the safe operation of the container.
40 Reefer Container FAQS
What Happens if a 40 Foot Reefer Loses Power?
If a 40 foot reefer loses power, the refrigeration system will stop working, and the internal temperature of the container will start to rise. The rate at which the temperature increases depends on factors like the initial set temperature, the insulation quality of the container, and the external ambient temperature. For perishable goods stored in the 40ft reefer container, this can quickly lead to spoilage. For example, fresh produce may start to rot, and frozen goods may begin to thaw. In the case of pharmaceuticals, a loss of power and subsequent temperature fluctuations can render the products ineffective or even dangerous. It’s crucial to have backup power sources or contingency plans in place to minimize the impact of a power outage on the cargo stored in a 40 reefer container.
Can I Use a Regular Household Generator to Power a 40 Reefer Container?
In most cases, a regular household generator is not suitable for powering a 40 reefer container. 40 reefer containers require a significant amount of power, especially during startup surges, and operate on specific voltage and phase requirements. Household generators typically have lower power capacities and are designed for single-phase, lower-voltage applications, such as powering home appliances. Using a household generator to power a 40 foot reefer can lead to insufficient power supply, damage to the generator or the container’s refrigeration system, and safety hazards. It’s recommended to use generators specifically designed for industrial or marine applications that can meet the power requirements of 40ft reefer containers.
How Can I Monitor the Power Consumption of My 40ft Reefer Container?
There are several ways to monitor the power consumption of a 40ft reefer container. Many modern refrigeration units for 40 reefer containers come with built-in monitoring systems that display real-time power consumption data. These systems can be accessed through a control panel on the container or remotely via a connected device. Additionally, external power meters can be installed between the power source and the 40 foot reefer to accurately measure the electricity usage. By monitoring the power consumption, operators can identify any abnormal spikes or inefficiencies in the system, take corrective actions, and manage their power costs more effectively.
Do Different Brands of 40 Reefer Container Have Different Power Requirements?
While the basic power requirements for 40 reefer containers follow industry standards, there can be some variations between different brands. Some brands may use more energy-efficient refrigeration systems or advanced insulation materials, which can result in lower power consumption. On the other hand, certain models may have additional features, such as enhanced climate control or advanced monitoring systems, that can increase the overall power requirements. However, these differences are usually within a reasonable range. When choosing a 40ft reefer container, it’s important to review the manufacturer’s specifications regarding power requirements to ensure compatibility with your intended power sources and to accurately estimate operating costs.
What Are the Backup Power Options for a 40 Foot Reefer?
There are several backup power options for a 40 foot reefer. One common option is an auxiliary diesel generator, which can be quickly started up in case of a primary power failure. Battery – powered backup systems are also available, which can provide temporary power to keep the refrigeration system running for a limited time. Some 40 reefer containers are now being equipped with uninterruptible power supply (UPS) units that can bridge short power outages and allow for a smooth transition to a backup power source. Additionally, in some locations, alternative energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines can be used in combination with battery storage systems to provide a sustainable backup power solution for 40ft reefer containers.