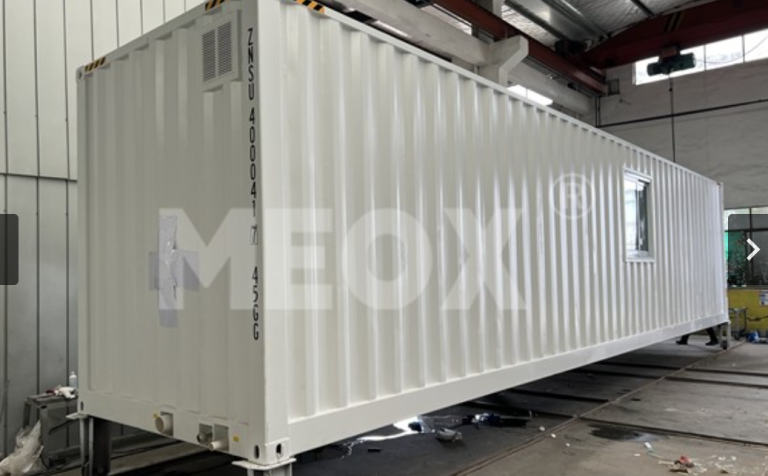
In the rapidly evolving landscape of energy storage, shipping container battery storage has emerged as a versatile and efficient solution. Among the various technologies powering these containers, lithium ion battery storage containers are at the forefront, offering high performance and reliability. Container energy storage systems, encapsulated within shipping containers, provide a convenient and scalable way to store and distribute electricity. The storage capacity of these batteries is a crucial factor that determines their applications, from powering remote communities to stabilizing the grid.

Factors Influencing Lithium Ion Battery Storage Container Capacities
Several elements play a role in determining the capacities of lithium ion battery storage containers within shipping container battery storage setups. The type and quality of lithium – ion cells used are fundamental. High – density lithium – ion cells can pack more energy into a given space, increasing the overall capacity of the container energy storage system. Additionally, the number of battery modules installed in a container directly impacts its capacity. A larger shipping container battery storage unit with more modules will naturally have a higher energy – storing ability. The design of the battery management system (BMS) also matters. An efficient BMS optimizes the charging and discharging processes, maximizing the usable capacity of the lithium ion battery storage container and ensuring its longevity.
Common Capacity Ranges of Shipping Container Battery Storage
Shipping container battery storage systems come in a wide range of capacities to suit different energy demands. Small – scale container energy storage units, often used for residential backup power or small commercial applications, might have capacities ranging from 50 to 500 kilowatt – hours (kWh). These units typically house a moderate number of lithium – ion battery packs within a lithium ion battery storage container. On the other hand, large – scale shipping container battery storage facilities designed for grid – scale applications can have capacities exceeding 100 megawatt – hours (MWh). These massive installations involve multiple lithium ion battery storage containers interconnected within large shipping containers, providing substantial energy reserves to support entire communities or balance the power grid during peak demand.
Scalability of Container Energy Storage Capacities
One of the significant advantages of container energy storage is its scalability, which directly relates to the storage capacities of shipping container battery storage systems. Users can start with a smaller lithium ion battery storage container and expand the system as their energy needs grow. By adding more battery modules or even entire containers, the overall capacity of the container energy storage setup can be increased incrementally. This scalability makes shipping container battery storage an attractive option for businesses and organizations with evolving energy requirements. Whether it’s a small business looking to expand its backup power capacity or a utility company planning for future grid – scale energy storage, the ability to scale container energy storage capacities offers flexibility and cost – effectiveness.
Impact of Capacity on Application of Lithium Ion Battery Storage Container
The capacity of a lithium ion battery storage container within a shipping container battery storage system dictates its suitable applications. A low – capacity container energy storage unit might be ideal for providing backup power to a single household during outages, ensuring essential appliances like refrigerators, lights, and medical devices remain operational. Medium – capacity shipping container battery storage systems can support small – to – medium – sized businesses, powering their operations during peak electricity rates or grid disruptions. High – capacity lithium ion battery storage containers, on the other hand, are crucial for large – scale applications such as integrating renewable energy sources into the grid. They store excess energy generated by wind farms or solar plants and release it when renewable production is low, stabilizing the overall container energy storage and distribution of electricity.
Shipping Container Battery Storage FAQS
How Do I Calculate the Required Capacity for My Container Energy Storage?
Calculating the required capacity for your container energy storage depends on your energy consumption needs. First, list all the devices or systems you want to power during a power outage or specific period. Determine their power ratings (in watts) and the duration (in hours) for which you need to run them. Multiply the power rating of each device by the number of hours of usage and sum up these values for all devices.
Can the Capacity of a Lithium Ion Battery Storage Container Be Increased After Installation?
In many cases, the capacity of a lithium ion battery storage container within a shipping container battery storage system can be increased after installation. If the container has been designed with scalability in mind, additional battery modules can often be added. However, this process requires careful consideration. You need to ensure that the existing battery management system can handle the increased load and that the electrical infrastructure within the container energy storage unit can support the new modules. It’s also important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and, in some cases, consult with professionals to ensure proper installation and integration. Improperly adding modules can lead to safety hazards or reduced performance of the shipping container battery storage system.
What Are the Safety Risks Associated with High – Capacity Shipping Container Battery Storage?
High – capacity shipping container battery storage systems with lithium ion battery storage containers do pose some safety risks. Overheating is a major concern, as a large number of batteries generate significant heat during charging and discharging. If not properly managed by the thermal management system within the container energy storage unit, overheating can lead to battery degradation, fires, or even explosions. There’s also the risk of electrical faults such as short – circuits, which can occur due to damaged wiring or malfunctioning components. Additionally, improper handling or installation of the batteries in a lithium ion battery storage container can increase the likelihood of safety incidents. To mitigate these risks, strict safety protocols, advanced monitoring systems, and regular maintenance of the shipping container battery storage setup are essential.
How Does the Lifespan of Batteries Relate to the Capacity of Shipping Container Battery Storage?
The lifespan of batteries in a shipping container battery storage system with lithium ion battery storage containers is closely related to the capacity. Frequent deep discharges (draining the battery to a very low level) and overcharging can significantly reduce the lifespan of lithium – ion batteries, regardless of the container’s overall capacity. When the container energy storage system is used in a way that repeatedly stresses the batteries, their ability to hold a charge (capacity) will degrade over time. On the other hand, proper management of the battery’s state of charge, such as keeping it within an optimal range during charging and discharging, can help maintain the capacity and extend the lifespan of the batteries in the shipping container battery storage unit. Regular maintenance and following the manufacturer’s recommendations also play a crucial role in preserving both the capacity and lifespan of the batteries.
Are There Any Government Incentives for Investing in High – Capacity Container Energy Storage?
Yes, many governments around the world offer incentives for investing in high – capacity container energy storage systems like shipping container battery storage with lithium ion battery storage containers. These incentives are aimed at promoting the adoption of clean energy storage technologies, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and stabilizing the power grid. Incentives can include tax credits, grants, subsidies, and feed – in tariffs. For example, some countries provide tax credits based on the installed capacity of the container energy storage system, which can significantly reduce the upfront investment cost for businesses and individuals. Others offer grants to support research and development in improving shipping container battery storage technologies and increasing their capacities. These government incentives make high – capacity container energy storage more attractive and accessible, driving the growth of the energy storage industry.