Farming in remote and off-grid areas often faces a major challenge: lack of reliable electricity. Whether it’s powering irrigation systems, refrigeration units, or basic lighting, energy access can be the deciding factor between crop failure and agricultural success. This is where solar containers for off-grid farming are transforming the landscape. These modular, portable units offer a sustainable, cost-effective, and low-maintenance solution for farmers who need power in remote locations.
In this article, we explore how solar containers work, their benefits for off-grid agriculture, and how they’re helping create a more resilient and productive farming future.
What Are Solar Containers for Off‑Grid Farming?
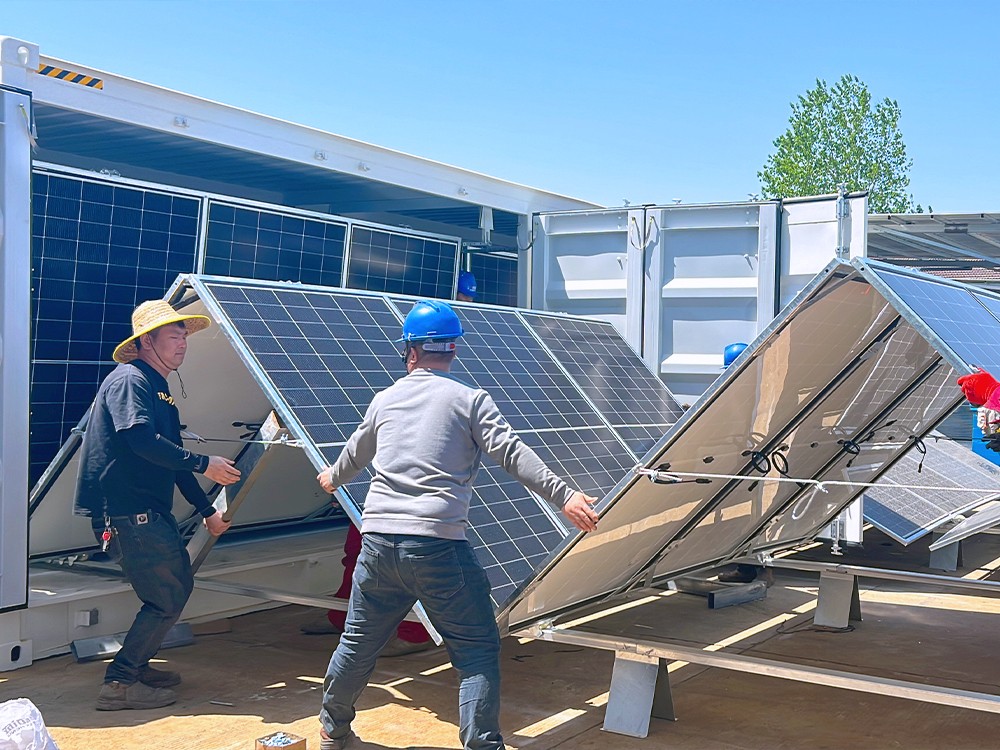
Solar containers are essentially modular energy systems built into shipping container-style enclosures. Equipped with solar panels, battery banks, inverters, and power management systems, they’re designed to generate, store, and distribute solar electricity—even in the most isolated environments.
For off-grid farming, these containers are a game-changer. Instead of waiting years (or never) for connection to the national grid, farmers can deploy a solar container in just days. Many of these units come fully pre-assembled, meaning once delivered to the site, they’re virtually plug-and-play. Depending on their configuration, they can power everything from water pumps and cold storage to fans, lights, sensors, and small machinery.
Key Benefits of Using Solar Containers for Off‑Grid Farming
One of the main advantages of solar containers is energy independence. In areas where grid power is unreliable or nonexistent, solar containers provide a reliable source of clean energy with minimal maintenance. They also reduce the need for diesel generators, which are noisy, expensive to operate, and harmful to the environment.
Here are some specific benefits for farmers:
Reliable irrigation: With solar-powered pumps, farmers can water crops on schedule, even in dry seasons.
Cold chain preservation: Produce like dairy, vegetables, or fish can be kept fresh with solar-powered refrigeration.
Nighttime operations: Lights powered by the container system can extend working hours and improve security.
Cost savings: After initial investment, solar power is free, significantly lowering long-term operational costs.
Environmental benefits: Solar containers reduce carbon emissions and protect soil and air quality.
Over time, these advantages directly translate into higher crop yields, reduced losses, and increased income for farmers in off-grid settings.
Use Cases of Solar Containers in Off‑Grid Farming
Solar containers can be customized for various agricultural needs, making them highly adaptable. Some real-world applications include:
- Irrigation Systems
Solar containers can power submersible or surface water pumps for irrigation. By connecting to drip or sprinkler systems, farmers can improve efficiency while conserving water. Some setups even include timed irrigation controlled by solar-charged sensors. - Refrigerated Storage
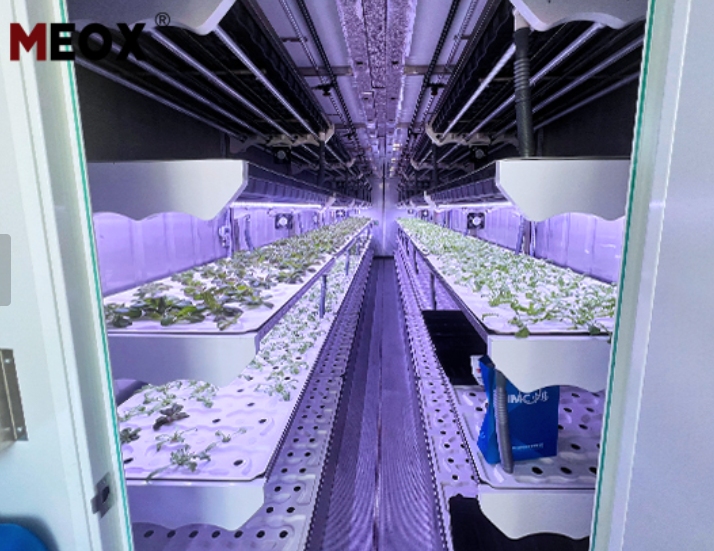
Perishable goods like fruits, milk, meat, and fish require cooling to stay fresh. Solar containers with integrated cold rooms allow farmers to store produce on-site until transportation is available. This helps reduce post-harvest waste and supports better pricing strategies. - Hydroponics and Vertical Farming
In innovative farming models like hydroponics, lighting and water circulation are essential. Solar containers provide the steady electricity needed to power LED grow lights, climate controls, and circulation pumps in off-grid greenhouses or shipping container farms. - Charging Stations and Rural Business Hubs
In addition to agricultural operations, solar containers can serve as power hubs in rural communities—charging phones, laptops, and even small tools. They can also power IT systems for farm data tracking, training centers, or agri-business operations.
Design and Components of Solar Containers for Farming
A typical solar container system is modular and scalable. Here’s what you’ll find inside:
Solar panels: Usually mounted on top of the container or deployed as a fold-out array.
Battery storage: High-capacity lithium or gel batteries store excess energy for use at night or during cloudy periods.
Inverter system: Converts DC from the panels to AC electricity usable by standard farming equipment.
Charge controller: Regulates the power input from panels to batteries, preventing overcharging.
Smart monitoring system: Enables farmers to track energy usage, battery levels, and performance via mobile app or display screen.
Optional extras: Some containers come with pre-installed pumps, refrigeration units, lighting kits, or communication modules for remote monitoring.
The entire system is often built into a rugged, weatherproof container to withstand harsh agricultural environments, including extreme heat, dust, and heavy rainfall.
Why Solar Containers Are the Future of Sustainable Agriculture
As climate change accelerates and energy access becomes more critical, solar containers represent a scalable and sustainable path forward. By decentralizing power generation, they allow smallholder farmers, cooperatives, and agribusinesses to achieve self-sufficiency and resilience in the face of environmental and economic challenges.
They’re also aligned with the global push for clean energy adoption, especially in developing regions where agriculture is the backbone of the economy but infrastructure is limited. With solar container solutions, governments, NGOs, and private enterprises can provide energy access that fuels productivity and empowers rural communities.
In addition, solar containers are compatible with carbon credit projects and green funding, making them eligible for subsidies or incentives aimed at renewable energy adoption.
Choosing the Right Solar Container for Your Farm
Not all solar containers are the same, so it’s important to choose a provider that understands agricultural needs. Key factors to consider include:
Energy output (measured in kWh/day)
Battery capacity and type
Load compatibility with farming equipment
Ease of transport and installation
After-sales support and technical training
Working with a trusted manufacturer or supplier can make all the difference. Look for companies that offer customizable solutions, remote monitoring, and performance warranties. Farmers should also ensure that their solar container is sized correctly for both current energy demands and future expansion.
Powering Growth with Solar Containers for Off‑Grid Farming
Solar containers are more than just an alternative power source—they’re an agricultural enabler. They offer an eco-friendly, reliable, and cost-effective energy solution for farmers operating far from the grid. Whether you’re growing vegetables in the savannah, managing dairy herds in highland pastures, or cultivating herbs in a desert greenhouse, solar containers make modern farming possible—anywhere, anytime.
By investing in this technology, farmers aren’t just adopting clean energy; they’re planting the seeds of long-term sustainability and rural development.