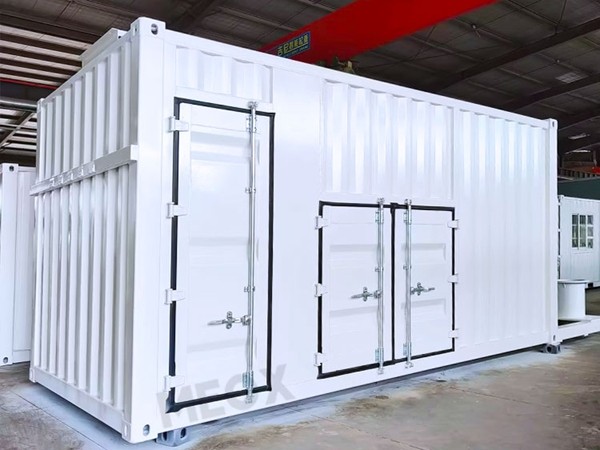
Stackable shipping containers have emerged as a revolutionary solution in the world of vertical farming, offering unprecedented opportunities for efficient and sustainable agricultural production. This modern trend combines the robustness and modularity of shipping containers with the space-efficiency of vertical farming, carving a niche for itself in urban agriculture.

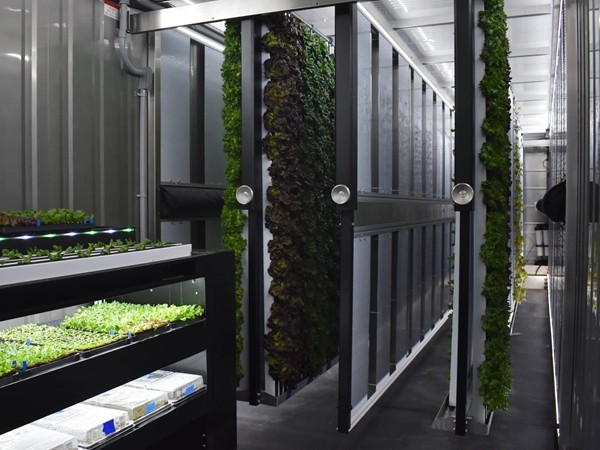
Vertical farming, a practice that involves cultivating crops in stacked layers, typically uses controlled-environment agriculture technology. This method has become essential in densely populated urban areas where traditional farming is not feasible. By incorporating stackable shipping containers into this equation, farmers can harness a dynamic and scalable agricultural system that is both eco-friendly and economically viable.
The primary advantage of using stackable shipping containers is their modularity. These containers can be transported worldwide, making them ideal for urban setups and food production in areas with limited arable land. They can be easily stacked and arranged to fit into tight urban spaces or underutilized areas such as rooftops and parking lots. This versatility supports year-round farming, independent of weather conditions, thanks to the controlled environment they provide.

Each container can be equipped with hydroponic, aeroponic, or aquaponic systems that minimize water usage and eliminate the need for soil, making them perfect for urban settings. These systems ensure that plants receive the right amount of nutrients, light, and water, contributing to higher yields compared to traditional farming methods. Additionally, by using LED lighting and advanced climate control systems, the plant growth cycle can be meticulously managed, allowing for multiple harvests per year.
Sustainability is another critical factor in the appeal of stackable shipping containers for vertical farming. Reusing decommissioned shipping containers reduces waste and repurposes industrial products, translating into a smaller carbon footprint for urban farms. The energy-efficient systems integrated within these containers further enhance their sustainability by optimizing resource usage.stackable shipping containers vertical farming
From an economic perspective, stackable shipping containers in vertical farming offer substantial benefits. The initial setup and operational costs can be high; however, the long-term savings from reduced transportation and water costs, coupled with the ability to produce food near urban centers, present a compelling financial case. The proximity to market reduces the need for transportation, cutting down emissions and making fresh produce more readily available to consumers, often enhancing its nutritional value.
Entrepreneurs venturing into this domain can leverage technology and data analytics to optimize crop yields and resource management. With the Internet of Things (IoT), sensors within these containers can monitor plant health, environmental conditions, and system efficiency in real-time. This data-driven approach allows for proactive management of resources, ensuring optimal growing conditions and maximizing productivity.
Experts and organizations focusing on urban sustainability recognize stackable shipping containers as a forward-thinking solution. Collaborations between city planners, agricultural tech firms, and environmental advocates are increasingly promoting these systems as a means to bolster urban food security and resilience. Educational programs and certifications are also being developed to train a new generation of farmers in this cutting-edge field.
Trust in these systems continues to grow as more successful case studies emerge. Cities like New York, Tokyo, and Amsterdam are already showcasing functional projects that testify to the viability of stackable shipping containers in urban agriculture. They exemplify how food can be produced efficiently and sustainably within urban spaces, setting a precedent for other cities worldwide to follow.
In summary, stackable shipping containers present a transformative approach to urban farming, marrying the strengths of modular design with the efficiencies of vertical farming. As technological advancements continue to refine these systems, their role in reshaping urban food landscapes will undoubtedly expand, offering a scalable and sustainable solution to some of the most pressing challenges in agriculture today.